deep-learning-from-scratch/ch06 at master · oreilly-japan/deep-learning-from-scratch · GitHub
「ゼロから作るDeep Learning ① (Pythonで学ぶディープラーニングの理論と実装)」 p.177~186 の写経です。
p.178によれば、過学習を抑える為、重みの初期値は
- できるだけ小さな値
- ≠0
- ランダム
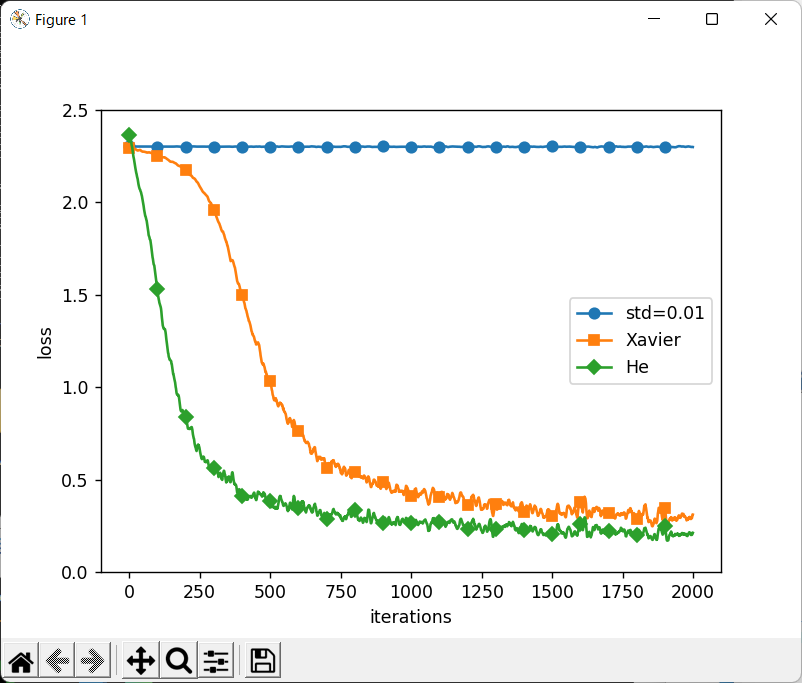
が良いらしく、更には「sigmoid関数にはXavier初期値」、 「relu関数にはHe初期値」が良いらしく、これにより、重みが広がりを持つようです。 (詳細は、本をご覧ください)
以下のpython scriptは、初期値によるlossの変化(効率化)を比較するものです。
# coding: utf-8 import os import sys import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import urllib.request import gzip from collections import OrderedDict def main(): # MNISTデータのdownload mymnist = MyMnist() (x_train, t_train, x_test, t_test) = mymnist.load_mnist() train_size = x_train.shape[0] batch_size = 128 max_iterations = 2000 weight_init_types = { 'std=0.01': 0.01, # 通常?は、標準偏差初期値 'Xavier': 'sigmoid', # sigmoidには、Xavier初期値 'He': 'relu' # reluには、He初期値 } optimizer = SGD(lr=0.01) # 確率的勾配降下法 networks = {} train_loss = {} for key, weight_type in weight_init_types.items(): networks[key] = \ MultiLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size_list=[100,100,100,100], output_size=10, weight_init_std=weight_type) train_loss[key] = [] # 訓練 print( "i std=0.01 Xavier He" ) for i in range(max_iterations): batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size) x_batch = x_train[batch_mask] t_batch = t_train[batch_mask] for key in weight_init_types.keys(): grads = networks[key].gradient(x_batch, t_batch) optimizer.update(networks[key].params, grads) loss = networks[key].loss(x_batch, t_batch) train_loss[key].append(loss) if i % 100 == 0: disp_cols = [str(i)] for key in weight_init_types.keys(): loss = networks[key].loss(x_batch, t_batch) disp_cols.append( str(loss) ) print( "\t".join( disp_cols ) ) my_plot = MyPlot() my_plot.disp_graph(max_iterations, weight_init_types, train_loss ) class MyPlot: def __init__(self): pass def disp_graph(self, max_iterations, weight_init_types, train_loss ): markers = {'std=0.01': 'o', 'Xavier': 's', 'He': 'D'} x = np.arange(max_iterations) for key in weight_init_types.keys(): plt.plot(x, self.smooth_curve(train_loss[key]), marker=markers[key], markevery=100, label=key ) plt.xlabel("iterations") plt.ylabel("loss") plt.ylim(0, 2.5) plt.legend() plt.show() # 損失関数のグラフを滑らかにする # http://glowingpython.blogspot.jp/2012/02/convolution-with-numpy.html def smooth_curve(self, x): window_len = 11 s = np.r_[x[window_len-1:0:-1], x, x[-1:-window_len:-1]] w = np.kaiser(window_len, 2) y = np.convolve(w/w.sum(), s, mode='valid') return y[5:len(y)-5] # 確率的勾配降下法 Stochastic Gradient Descent class SGD: def __init__(self, lr=0.01): self.lr = lr # lrは学習率 def update(self, params, grads): for key in params.keys(): params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key] class MyMnist: def __init__(self): pass def load_mnist(self): data_files = self.download_mnist() # convert numpy dataset = {} dataset['train_img'] = self.load_img( data_files['train_img'] ) dataset['train_label'] = self.load_label(data_files['train_label']) dataset['test_img'] = self.load_img( data_files['test_img'] ) dataset['test_label'] = self.load_label(data_files['test_label']) for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'): dataset[key] = dataset[key].astype(np.float32) dataset[key] /= 255.0 for key in ('train_label','test_label'): dataset[key]=self.change_one_hot_label( dataset[key] ) return (dataset['train_img'], dataset['train_label'], dataset['test_img'], dataset['test_label'] ) def change_one_hot_label(self,X): T = np.zeros((X.size, 10)) for idx, row in enumerate(T): row[X[idx]] = 1 return T def download_mnist(self): url_base = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/' key_file = {'train_img' :'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 'train_label':'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz', 'test_img' :'t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 'test_label' :'t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz' } data_files = {} dataset_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) for data_name, file_name in key_file.items(): req_url = url_base+file_name file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name request = urllib.request.Request( req_url ) response = urllib.request.urlopen(request).read() with open(file_path, mode='wb') as f: f.write(response) data_files[data_name] = file_path return data_files def load_img( self,file_path): img_size = 784 # = 28*28 with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f: data = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16) data = data.reshape(-1, img_size) return data def load_label(self,file_path): with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f: labels = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8) return labels # 全結合による多層ニューラルネットワーク class MultiLayerNet: def __init__( self, input_size, # 入力size MNISTの場合 784 hidden_size_list, # 隠れ層のneuron数 例[100,100,100] output_size, # 出力size MNISTの場合 10 activation='relu', # 活性化関数 'relu' or 'sigmoid' weight_init_std='relu',# ※ weight_decay_lambda=0):# Weight Decay (L2ノルム)の強さ # ※ weight_init_std : # 重みの標準偏差を指定(e.g. 0.01) # 'relu'または'he'を指定した場合は「Heの初期値」 # 'sigmoid'または'xavier'を指定した場合は「Xavierの初期値」 self.input_size = input_size self.output_size = output_size self.hidden_size_list = hidden_size_list self.hidden_layer_num = len(hidden_size_list) self.weight_decay_lambda = weight_decay_lambda self.params = {} # 重みの初期化 self.__init_weight(weight_init_std) # レイヤの生成 activation_layer = {'sigmoid': Sigmoid, 'relu': Relu} self.layers = OrderedDict() for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num+1): self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)] = \ Affine(self.params['W' + str(idx)], self.params['b' + str(idx)]) self.layers['Activation_function' + str(idx)] = \ activation_layer[activation]() idx = self.hidden_layer_num + 1 self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)] = \ Affine(self.params['W' + str(idx)], self.params['b' + str(idx)]) self.last_layer = SoftmaxWithLoss() # 重みの初期値設定 def __init_weight(self, weight_init_std): all_size_list = \ [self.input_size] + self.hidden_size_list + [self.output_size] for idx in range(1, len(all_size_list)): scale = weight_init_std if str(weight_init_std).lower() in ('relu', 'he'): # ReLUを使う場合の初期値 scale = np.sqrt(2.0 / all_size_list[idx - 1]) elif str(weight_init_std).lower() in ('sigmoid', 'xavier'): # sigmoidを使う場合の初期値 scale = np.sqrt(1.0 / all_size_list[idx - 1]) self.params['W' + str(idx)] = \ scale * np.random.randn(all_size_list[idx-1], all_size_list[idx]) self.params['b' + str(idx)] = np.zeros(all_size_list[idx]) def predict(self, x): for layer in self.layers.values(): x = layer.forward(x) return x # 損失関数を求める def loss(self, x, # 入力データ t):# 教師ラベル y = self.predict(x) weight_decay = 0 for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num + 2): W = self.params['W' + str(idx)] weight_decay += 0.5 * self.weight_decay_lambda * np.sum(W ** 2) return self.last_layer.forward(y, t) + weight_decay def accuracy(self, x, t): y = self.predict(x) y = np.argmax(y, axis=1) if t.ndim != 1 : t = np.argmax(t, axis=1) accuracy = np.sum(y == t) / float(x.shape[0]) return accuracy # 勾配を求める (数値微分) def numerical_gradient(self, x, t): loss_W = lambda W: self.loss(x, t) grads = {} for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num+2): grads['W' + str(idx)] = \ self._numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W' + str(idx)]) grads['b' + str(idx)] = \ self._numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b' + str(idx)]) return grads def _numerical_gradient(self, f, x): h = 1e-4 # 0.0001 grad = np.zeros_like(x) it = np.nditer(x, flags=['multi_index'], op_flags=['readwrite']) while not it.finished: idx = it.multi_index tmp_val = x[idx] x[idx] = tmp_val + h fxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h) x[idx] = tmp_val - h fxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h) grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2*h) x[idx] = tmp_val # 値を元に戻す it.iternext() return grad # 勾配を求める (誤差逆伝搬法) def gradient(self, x, t): # forward self.loss(x, t) # backward dout = 1 dout = self.last_layer.backward(dout) layers = list(self.layers.values()) layers.reverse() for layer in layers: dout = layer.backward(dout) # 設定 grads = {} for idx in range(1, self.hidden_layer_num+2): grads['W' + str(idx)] = \ self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)].dW + \ self.weight_decay_lambda * self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)].W grads['b' + str(idx)] = self.layers['Affine' + str(idx)].db return grads class Relu: def __init__(self): self.mask = None def forward(self, x): self.mask = (x <= 0) out = x.copy() out[self.mask] = 0 return out def backward(self, dout): dout[self.mask] = 0 dx = dout return dx class Sigmoid: def __init__(self): self.out = None def forward(self, x): out = sigmoid(x) self.out = out return out def backward(self, dout): dx = dout * (1.0 - self.out) * self.out return dx class Affine: def __init__(self, W, b): self.W =W self.b = b self.x = None self.original_x_shape = None # 重み・バイアスパラメータの微分 self.dW = None self.db = None def forward(self, x): # テンソル対応 self.original_x_shape = x.shape x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1) self.x = x out = np.dot(self.x, self.W) + self.b return out def backward(self, dout): dx = np.dot(dout, self.W.T) self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, dout) self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0) dx = dx.reshape(*self.original_x_shape) return dx class SoftmaxWithLoss: def __init__(self): self.loss = None self.y = None # softmaxの出力 self.t = None # 教師データ def forward(self, x, t): self.t = t self.y = self.softmax(x) self.loss = self.cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t) return self.loss def softmax(self,x): x = x - np.max(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True) # オーバーフロー対策 return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=-1, keepdims=True) def cross_entropy_error(self, y, t): if y.ndim == 1: t = t.reshape(1, t.size) y = y.reshape(1, y.size) # 教師データがone-hot-vectorの場合、正解ラベルのインデックスに変換 if t.size == y.size: t = t.argmax(axis=1) batch_size = y.shape[0] return -np.sum(np.log(y[np.arange(batch_size), t] + 1e-7)) / batch_size def backward(self, dout=1): batch_size = self.t.shape[0] # 教師データがone-hot-vectorの場合 if self.t.size == self.y.size: dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size else: dx = self.y.copy() dx[np.arange(batch_size), self.t] -= 1 dx = dx / batch_size return dx if __name__ == '__main__': main()
↑こう書くと、↓こう表示されます。
(dl_scratch) C:\Users\end0t\tmp\deep-learning-from-scratch\ch06>python foo.py i std=0.01 Xavier He 0 2.3025004704494005 2.2944839686050837 2.3653180242752265 100 2.302454057219614 2.262232616944392 1.423335924549919 200 2.3036850103449593 2.1885701331268885 0.8922211412264922 300 2.3016946285904103 1.9951984874523245 0.5921122127049883 400 2.3023076862028184 1.5446343436237382 0.40275908822140105 500 2.3030326901257485 1.1345704960672047 0.43646367986152734 600 2.301907296081413 0.7156987132105668 0.3053186464209969 700 2.3033136374489893 0.48499635572109423 0.17792225418744217 800 2.3005787741577275 0.5644043961354724 0.34814906298688486 900 2.303748175006521 0.6012669563754791 0.3043807980209645 1000 2.302643527159904 0.48081435514697207 0.27306946946391025 1100 2.297993101564411 0.38269275507390704 0.3207061269442881 1200 2.3055223181126547 0.38107335902028217 0.22529239435114604 1300 2.304165004571269 0.3188476087654375 0.18484296010456175 1400 2.2957005728712074 0.2831411390906005 0.20438082403853383 1500 2.3043031319472287 0.30482817306281096 0.20284927100771363 1600 2.3077019241695296 0.29383020286123773 0.17759237769208688 1700 2.2960884184185426 0.41951974165910566 0.26643741166574597 1800 2.299928249921105 0.2764734085240914 0.2112177030146325 1900 2.2992910824123762 0.46042525877196677 0.32704587115374617